
Microdiscectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation
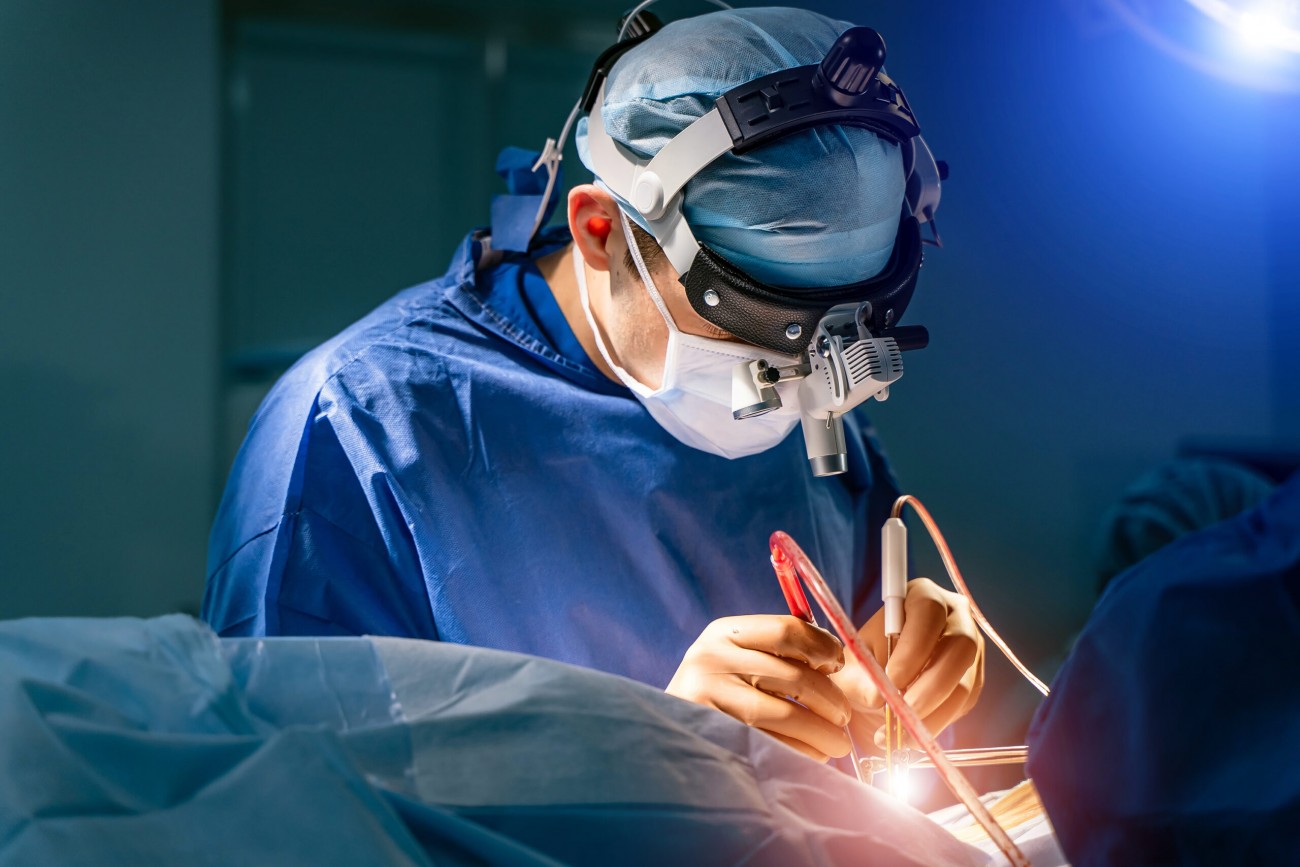
Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to treat lumbar disc herniation. Using an operating microscope and specialized microsurgical instruments, the surgeon removes the herniated portion of the disc that is compressing the spinal nerve. This technique offers significant advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster recovery.
What is Microdiscectomy?
How Does Lumbar Disc Herniation Occur?
The lumbar spine consists of vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs that act as cushions. Each disc has a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a soft gel-like center (nucleus pulposus). When the outer layer weakens or tears, the inner material can bulge or leak out, pressing on nearby spinal nerves. This compression causes the characteristic pain, numbness, and weakness associated with disc herniation.
When is Microdiscectomy Recommended?
Microdiscectomy is typically considered when:
- Conservative treatments (medication, physical therapy, injections) have failed after 6-12 weeks
- Leg pain (sciatica) is more severe than back pain
- Neurological symptoms are present (weakness, numbness, reflex changes)
- MRI confirms disc herniation correlating with clinical symptoms
- Cauda equina syndrome requires emergency surgery
- Quality of life is significantly affected despite conservative care

Symptoms Treated by Microdiscectomy
- Severe sciatic pain radiating down the leg
- Numbness or tingling in the leg, foot, or toes
- Muscle weakness in the leg or foot
- Burning or electric shock sensations
- Pain that worsens with sitting, bending, or coughing
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods
The Microdiscectomy Procedure
Pre-operative Preparation
- Comprehensive neurological examination
- MRI to precisely locate the herniation
- Pre-operative testing and medical clearance
- Discussion of expectations and potential risks
Surgical Technique
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia for patient comfort
- Positioning: Patient positioned face-down on specialized table
- Incision: Small incision (2-3 cm) directly over the affected disc level
- Muscle Retraction: Muscles gently moved aside without cutting
- Microscope: Operating microscope provides magnified, illuminated view
- Bone Removal: Minimal bone (lamina) removed if needed for access
- Nerve Protection: Compressed nerve carefully retracted
- Disc Removal: Herniated disc fragment removed
- Closure: Layers closed with absorbable sutures
Duration
The procedure typically takes 45-90 minutes depending on complexity.
Advantages of Microdiscectomy
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incision means less tissue trauma
- Better Visualization: Microscope provides superior view of structures
- Nerve Protection: Precise technique minimizes nerve manipulation
- Less Blood Loss: Reduced bleeding during surgery
- Faster Recovery: Most patients go home same day or next day
- Quick Pain Relief: Leg pain often improves immediately
- Early Return to Activities: Back to work in 2-6 weeks typically
- High Success Rate: 85-95% of patients experience significant improvement
Recovery After Microdiscectomy
First Few Days
- Most patients discharged same day or within 24 hours
- Walking encouraged within hours of surgery
- Mild incision discomfort managed with medication
- Leg pain typically significantly improved
First Few Weeks
- Avoid bending, lifting, and twisting
- Short walks multiple times daily
- Gradual increase in activity level
- Follow-up appointment at 2 weeks
Long-term Recovery
- Physical therapy may begin at 4-6 weeks
- Return to desk work: 2-4 weeks
- Return to physical work: 6-12 weeks
- Full recovery: 3-6 months
Success Rates and Outcomes
Microdiscectomy has excellent outcomes when performed for appropriate indications:
- 85-95% of patients report significant pain relief
- Leg pain improvement is typically more dramatic than back pain
- Most patients return to their previous activity level
- Recurrent disc herniation occurs in approximately 5-10% of cases
Why Choose Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk?
- Extensive experience with minimally invasive spine surgery
- Advanced microsurgical techniques and equipment
- Comprehensive pre-operative evaluation
- Personalized surgical planning for each patient
- Excellent track record of successful outcomes
Schedule Your Consultation
If you're suffering from lumbar disc herniation that hasn't responded to conservative treatment, microdiscectomy may provide the relief you need. Contact us to discuss your options with Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does the surgery take?
A typical microdiscectomy takes 45-90 minutes. More complex cases involving multiple levels or revision surgery may take longer.
Will I need to stay in the hospital?
Most patients go home the same day or the following morning. Overnight observation may be recommended for some patients.
When can I return to work?
Desk work: typically 2-4 weeks. Light physical work: 4-6 weeks. Heavy physical labor: 8-12 weeks. Your specific timeline will be discussed based on your job requirements.
Can the disc herniate again?
Recurrent herniation at the same level occurs in approximately 5-10% of patients over their lifetime. Proper body mechanics and core strengthening can help reduce this risk.
What is the difference between microdiscectomy and endoscopic discectomy?
Both are minimally invasive techniques. Microdiscectomy uses an operating microscope through a small open incision, while endoscopic discectomy uses a camera through an even smaller incision. The choice depends on the specific herniation type and surgeon experience.
Other Treatments

Spine Surgery
Surgical treatment of spine and spinal cord diseases

Deformity Surgery
Deformity surgery is the surgical correction of scoliosis, kyphosis, and spinal imbalance. Effective treatment is achieved with modern techniques and implants. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's expertise in complex deformity surgery.

Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Endoscopic spine surgery is a minimally invasive technique performed through an 8 mm incision. Same-day discharge and rapid recovery are possible for lumbar and cervical disc herniations. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's endoscopic surgery expertise.
Peripheral Nerve Surgery
Peripheral nerve surgery treats nerve compressions, injuries, and tumors. Carpal tunnel, cubital tunnel, and nerve tumors are treated surgically. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's nerve surgery expertise.
Reviewed by: Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk, Neurosurgeon
Last updated:
