
Thoracic Disc Herniation
Thoracic disc herniation occurs when one of the discs in the mid-back (thoracic) spine ruptures and compresses the spinal cord or nerve roots. It accounts for less than 1% of all disc herniations and is rare. Due to the stabilization provided by the rib cage, disc movement is limited in this region, but when herniation occurs, it can cause serious symptoms.
What Is Thoracic Disc Herniation?
Causes of Thoracic Disc Herniation
- Disc degeneration: Age-related wear
- Trauma: Falls, accidents, or sudden strain
- Repetitive micro-trauma: Prolonged poor posture
- Genetic factors: Familial predisposition
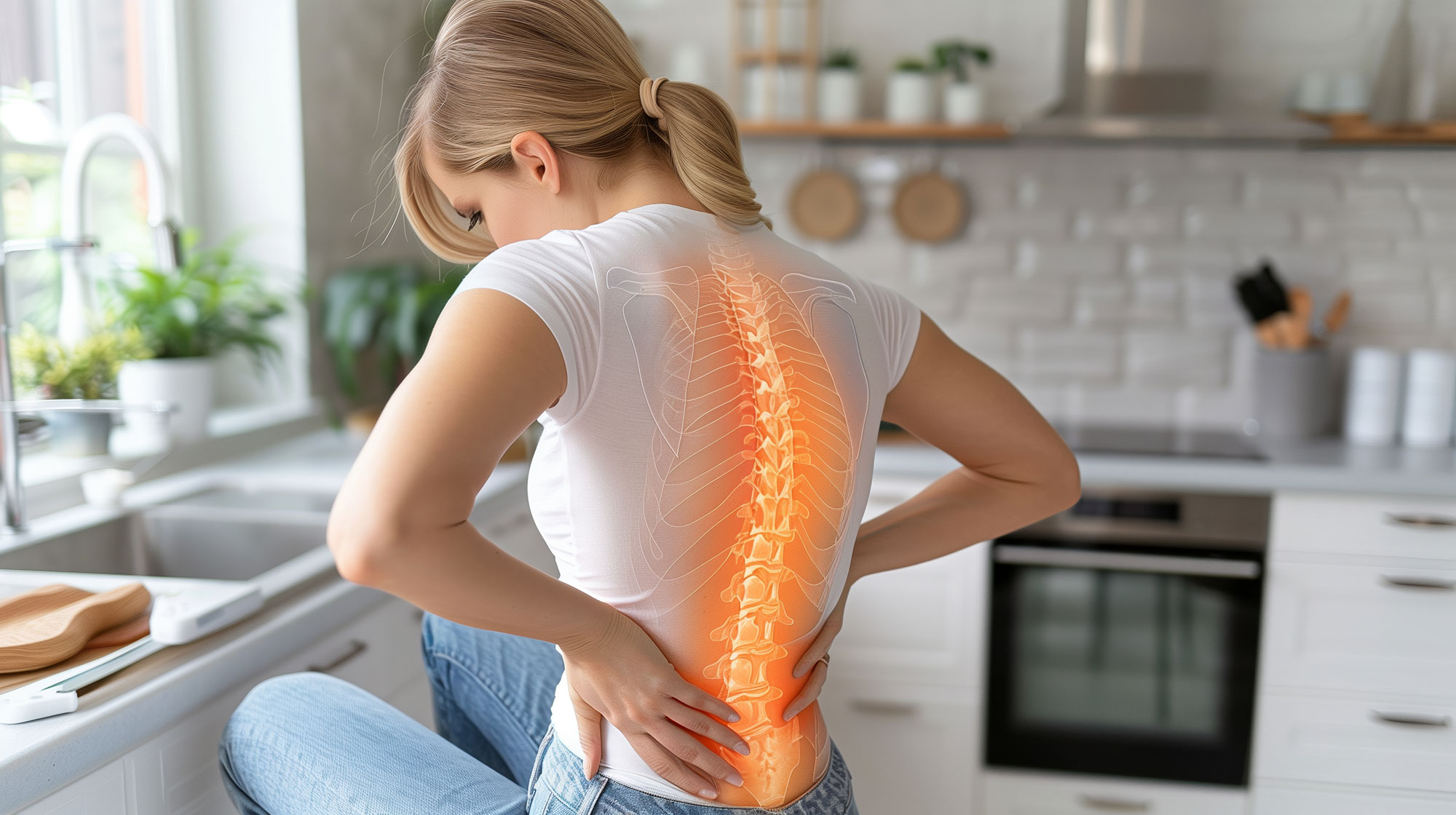
Symptoms
- Mid-back pain: Worsens with movement, improves with rest
- Radiating chest pain: Band-like, girdle pain
- Radiating abdominal pain: May mimic internal organ diseases
- Leg weakness: With spinal cord compression
- Walking difficulty: Spastic gait
- Bladder/bowel dysfunction: In advanced cases
- Numbness: Sensory loss in trunk or legs
Important Warning
Thoracic disc herniation symptoms may mimic heart, lung, or abdominal conditions. Comprehensive evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis
- Thoracic MRI: Assessment of herniation location and spinal cord compression
- CT scan: Visualization of calcified discs and bone details
- CT myelography: Detailed evaluation of spinal cord compression
- Neurological examination: Motor and sensory function assessment
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
First-line treatment option for patients with mild symptoms:
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Activity modification
- Epidural injections
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is required for spinal cord compression, progressive neurological deficits, or severe pain:
Posterior Approaches
- Transpedicular approach: Through the pedicle bone bridge
- Costotransversectomy: With rib removal
- Lateral extracavitary approach: Provides wide visualization
Thoracoscopic Surgery
Minimally invasive video-assisted thoracic surgery. Preferred in suitable cases.
Anterior (Transthoracic) Approach
Approach from the front by opening the chest cavity. May be necessary for large central herniations.
Post-Operative Care
- Hospital stay: 3-7 days
- Mobilization: Day 1-2
- Return to work: 4-8 weeks
- Physical therapy: After 4-6 weeks
Why Choose Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk?
Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk is experienced in the rare field of thoracic disc surgery. He provides safe treatment using minimally invasive techniques and microsurgery.
Find Out the Cause of Your Back Pain
Schedule an appointment for disc and spinal cord evaluation with thoracic MRI.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is thoracic disc herniation dangerous?
Herniations causing spinal cord compression can lead to permanent neurological damage if left untreated.
Is thoracic disc surgery difficult?
It is technically challenging due to the anatomy of the thoracic region, but safe outcomes are achieved by experienced surgeons.
Can it heal without surgery?
Conservative treatment may be sufficient for mild symptoms and cases without spinal cord compression.
Other Treatments

Spine Surgery
Surgical treatment of spine and spinal cord diseases

Deformity Surgery
Deformity surgery is the surgical correction of scoliosis, kyphosis, and spinal imbalance. Effective treatment is achieved with modern techniques and implants. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's expertise in complex deformity surgery.

Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Endoscopic spine surgery is a minimally invasive technique performed through an 8 mm incision. Same-day discharge and rapid recovery are possible for lumbar and cervical disc herniations. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's endoscopic surgery expertise.
Peripheral Nerve Surgery
Peripheral nerve surgery treats nerve compressions, injuries, and tumors. Carpal tunnel, cubital tunnel, and nerve tumors are treated surgically. Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk's nerve surgery expertise.
Reviewed by: Prof. Dr. Salim Şentürk, Neurosurgeon
Last updated:
